Ecological conditions force us to think in an environmentally friendly and energy- saving manner. These concerns lead to various measures easily illustrated in the area of energy-saving lighting solutions based both on the more economical lighting source as well as how these sources are used. This is one reason why the focus is on LED lighting and the demand-oriented use of light sources in general, or the combination of both. For example, for a radiant power of 600 lm luminous flux, the LED lamp requires only the single-digit electrical power of about 5 W to 8 W in comparison with a classic 60W incandescent bulb.
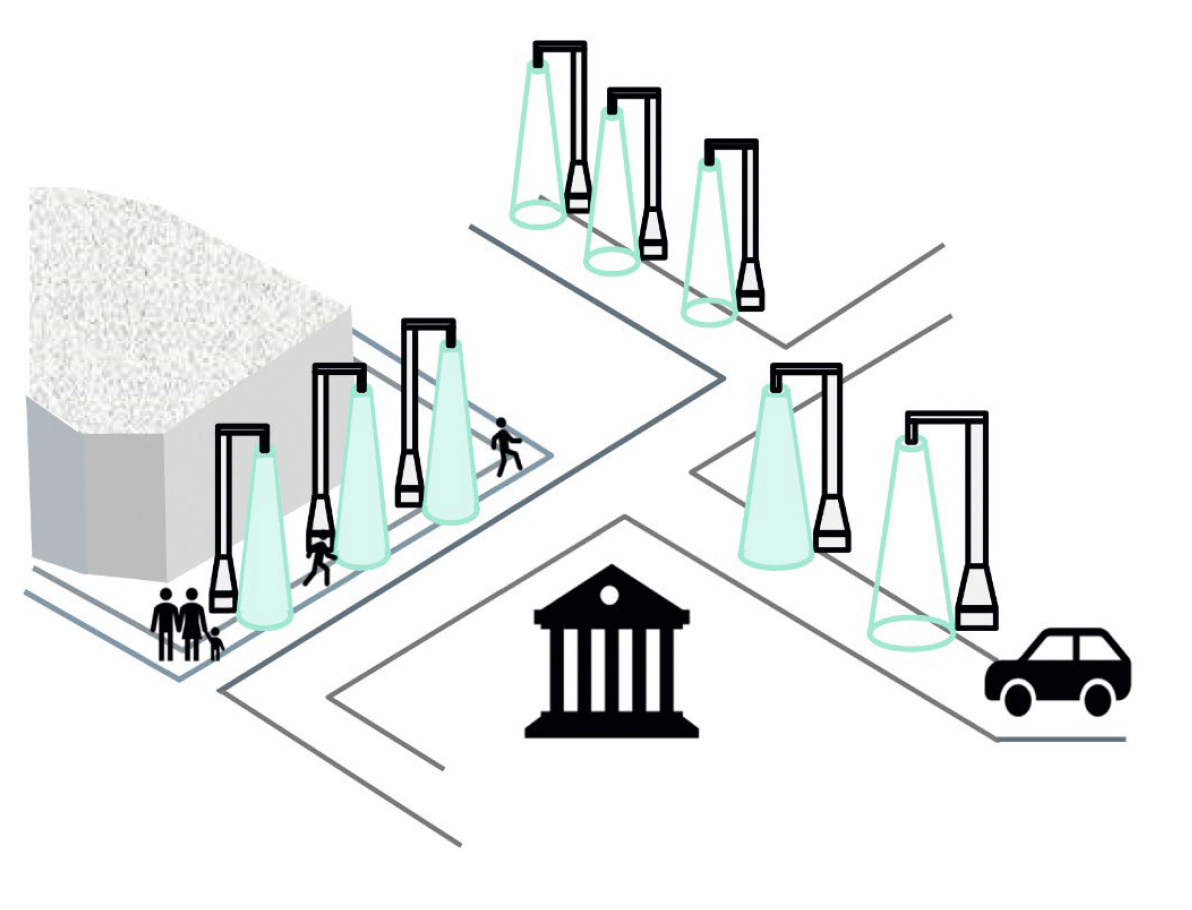
This is already an important step in the right direction, which can be further combined and increased with the effective, on-demand use of lighting, as reflected in the Light- on-Demand concept. Modern Doppler radar sensors that can detect moving objects such as people and vehicles, their direction and speed at a distance of several meters are ideal for this purpose. Special radar sensors with more intelligent evaluation algorithms can, for example, also determine the exact distance and angle relative to the sensor. These physical quantities can then be used to control assemblies that trigger an associated desired lighting response.
From this perspective, lighting streets and sidewalks can be controlled and switched on and off as needed, ensuring function for purpose and safety. Such a system can be applied equally well in town or cities and their pedestrian zones. In the latter, the rows of shop windows can also be analogously operated so that only those shop windows are fully illuminated where there are people nearby. Additional lamps can be switched on at the crosswalk when pedestrians are crossing a street.
Traffic flows can also be monitored and controlled with radar in order to direct high traffic volumes to other roads by switching traffic lights accordingly.
The lighting of parking garages and underground garages can also be used for traffic guidance during the day and night. Integrated radar modules in lamps can be used in a user-friendly way by switching them brighter than the rest of the lighting where the vehicle is driving or should be driving. Such a system can be designed so that only the used area is fully illuminated.
Modern radar sensors enable these lighting concepts in direct interaction with lamps or also via radio networks so that entire areas can be controlled accordingly, which can then also be influenced or configured remotely from a control center.